G Suite is an online collection of productivity, collaboration, and cloud computing tools created by Google for consumer and business use. The consumer suite is a free simplified version while the business suite adds lots of advanced features and is ideal for multiple users.
What is Included with G Suite?
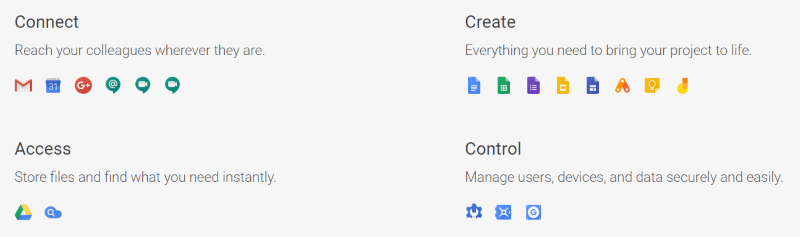
G Suite includes:
- Connect – Gmail, Calendar, Google+, Hangouts Chat, Hangouts Meet, Hangouts Meet hardware
- Create – Docs, Sheets, Forms, Slides, Sites, App Maker, Keep, Jamboard
- Access – Drive, Cloud Search
- Control – Admin, Vault, Mobile
The Business suite costs $5-$10 per user depending on the features you need. It adds custom email addresses, more cloud options, more administrative tools and settings, and 24/7 support.
One of the advantages of G Suite is it’s on Google’s servers. This helps keep the data secure and Google makes backups for you. The data itself is saved instantly.
You can access it from anywhere that you have an Internet connection and you can share specific files with your team or anyone you wish to collaborate with – making it a great tool for collaboration. The office apps can be used offline by installing the Chrome extension and admins can set up offline policies.
Another advantage is Google Analytics. You can check who’s using email, the number of Hangouts they’ve used, the amount of space they’ve used in the Google Drive, etc.
Setting Up G Suite for Your Business
Creating a G Suite account automatically gives you access to all of the apps for the suite you choose. You can set it up for a single person or a team of various sizes. I’m setting up an account for a small team. The setup for the other accounts is similar.
Set up Your G Suite Account
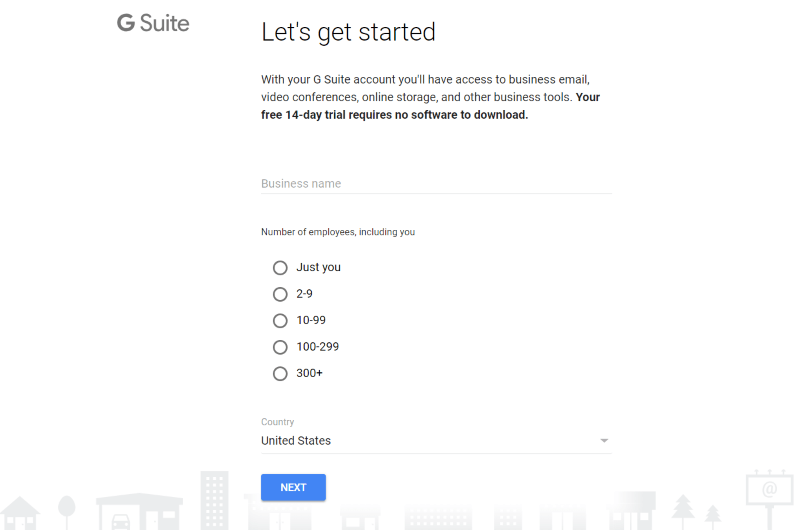
Create a G Suite account. You’ll start with a free trial. Add your business name, select the number of employees, and your country. Click Next and provide your contact info.
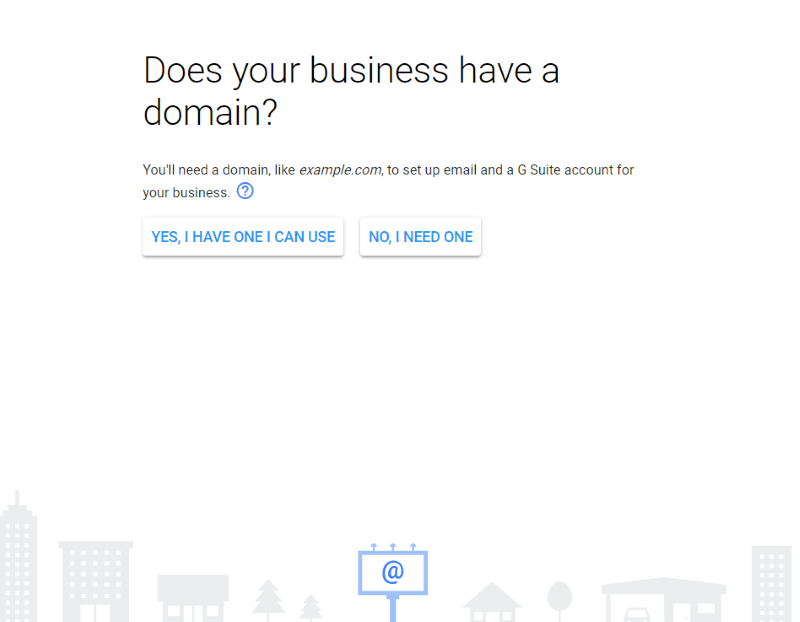
Add your business domain. If you don’t have one you’ll have the opportunity to get one here. Add your secondary email address.
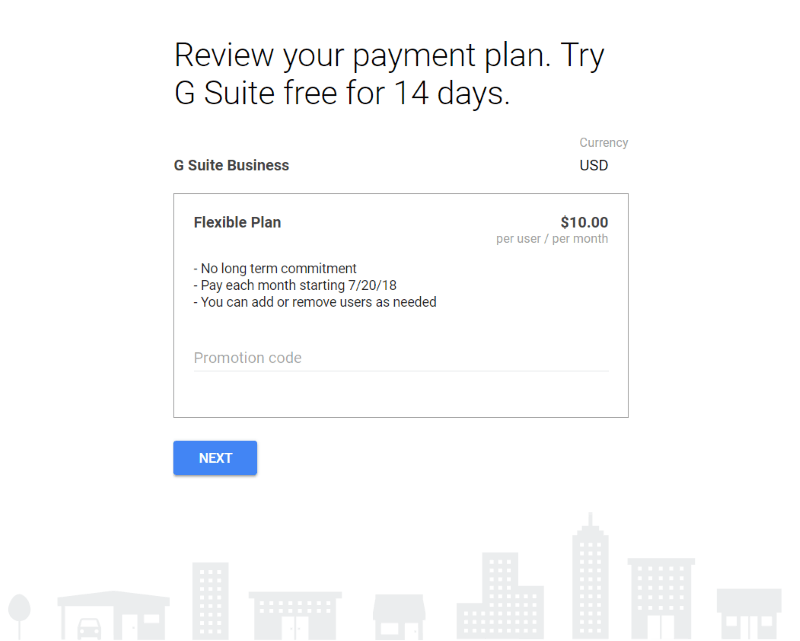
Create your login, click Next. Here, you’ll choose your plan and review your account settings.



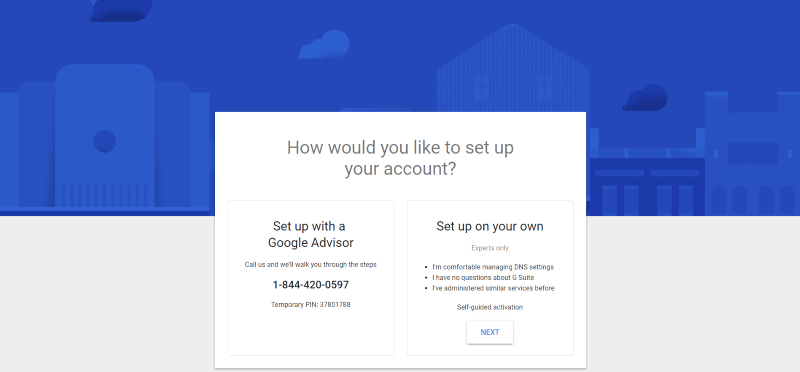
Once your account is created you’ll have the opportunity to set up the account with a Google advisor or set it up on your own. If you chose to set it up yourself you’ll need to be familiar with DNS. It’s not that difficult to do the setup yourself. It actually gives several options and examples for each one.

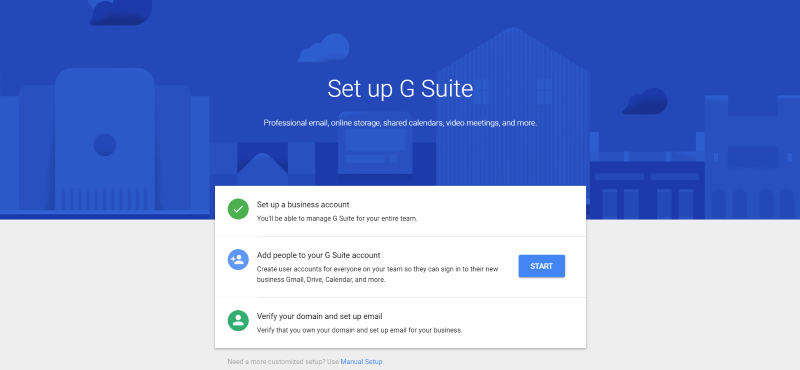
If you choose to set up my account manually, click Start next to Add people to your G Suite account to create user accounts for your team.

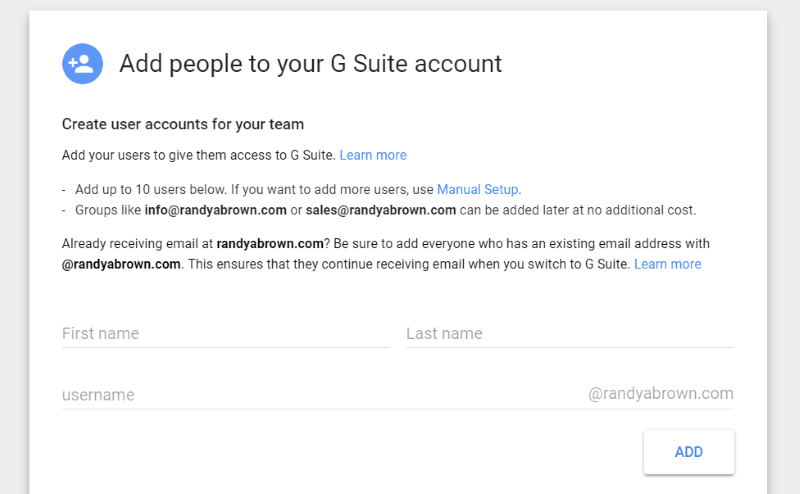
Add the users that have an email address from your domain. Google will contact your host to verify that you own the domain.

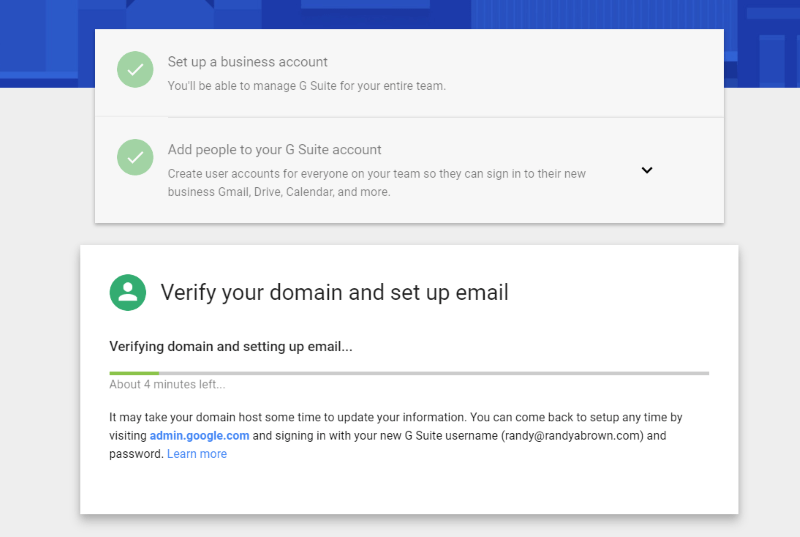
This will open your hosting account where you can authorize access and verify. Once the domain is verified all of the emails will be forwarded to G Suite. If it can’t verify automatically you’ll have to perform this step manually. Fortunately, there are several options.

To verify your domain manually with DNS, select this option and go to your domain hosting and click DNS.


Click Add and paste in the Google authorization code that Google provides. Go back to the G Suite setup and click to verify.
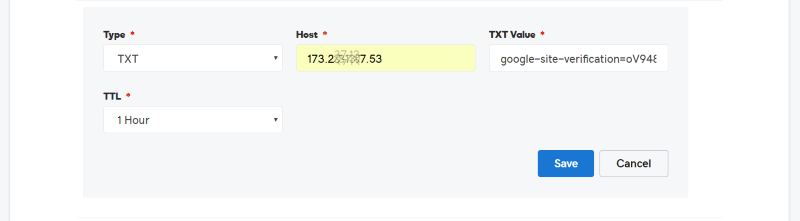

Another option is to add a meta tag or HTML to your website. Select this option and copy and paste the code into your header, and then click to verify. I found this to be the fastest option.
Admin Console
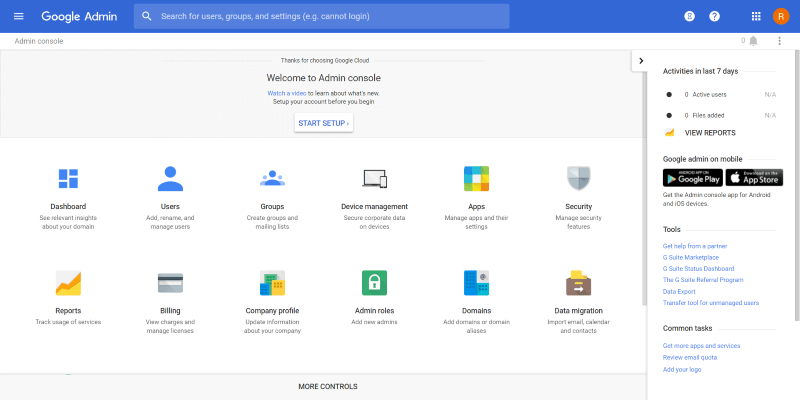

Once the account is verified you’ll be able to log into the admin console. Here you can set up users, groups, devices, apps, security, company profile, admin roles, domains, data migration, etc. You can also view reports and get support.
Company Profile
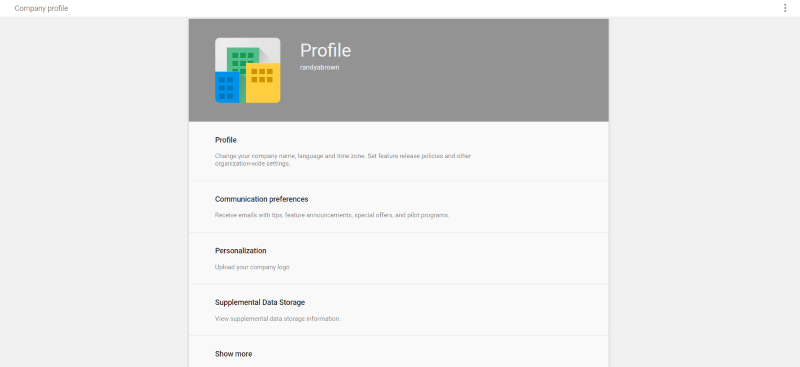

The Company Profile area is where you set up the company name, language, time zone, communication preferences, logo, create custom URL’s, etc. Use this to brand you G Suite account so when your team members are added the account will look familiar to them.
Add Users
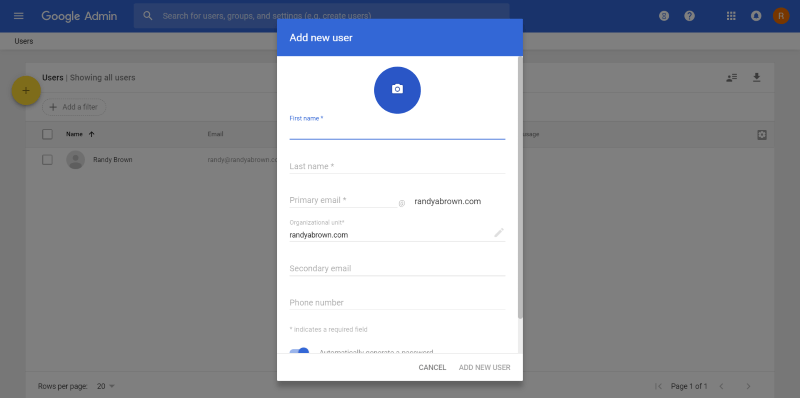

Click Users in the Admin Console and then hover over the yellow circle to add new users. You can add them one at a time or upload them in bulk as a CSV file.
Groups
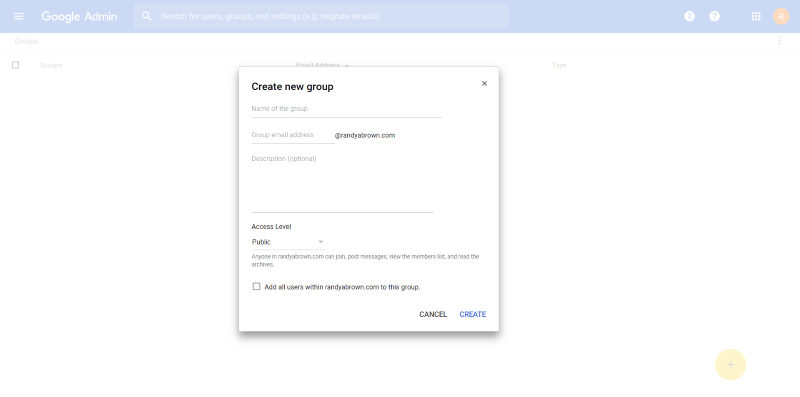

Groups are an easy way to define departments within the company and creates a communication channel for the group members. Groups can have as many members as you want and you can add the same users to multiple groups.
Device Management
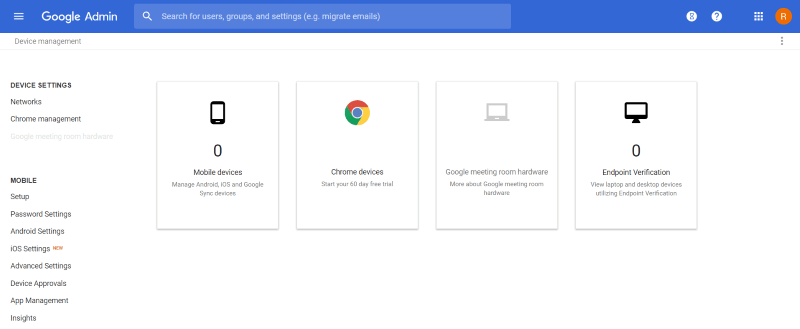

Device Management lets you set up the mobile devices that are allowed to access your G Suite account. You can manage Android and iOS devices, set up Chrome devices, meeting room hardware, and view laptops and desktops using endpoint verification. You can approve, block, wipe the device, wipe the account, delete, show the audit events, and export the data.
Apps
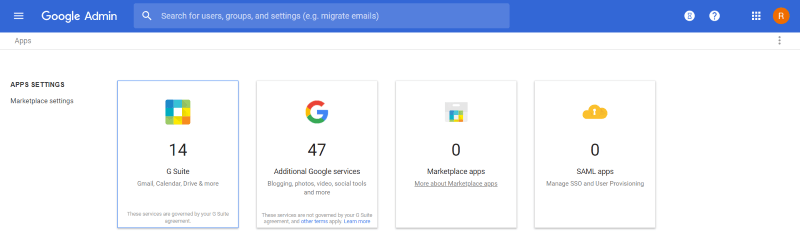

Apps is one of the most important features of G Suite. This includes email, contacts, calendar, Google Drive, Google +, Hangouts, and lots more. This screen lets you choose what’s available to users and what’s not. They are enabled by default. If you want to make customizations for the primary apps click G Suite.
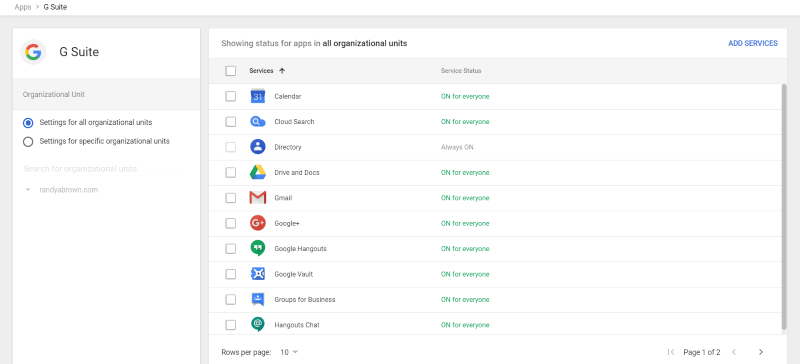

This is the list of the primary apps. You can set them up for all or specific organizational units and add more services.
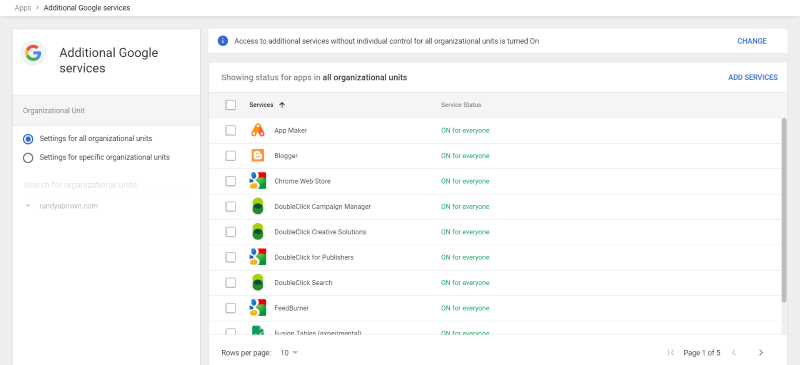

The Additional Google services includes the apps that are more specialized. This includes AdSense, FeedBurner, Blogger, AdWords, Analytics, and lots more. They’re also enabled by default. Click on each service to disable them. You can also select them for all or specific organizational units.
Admin Roles
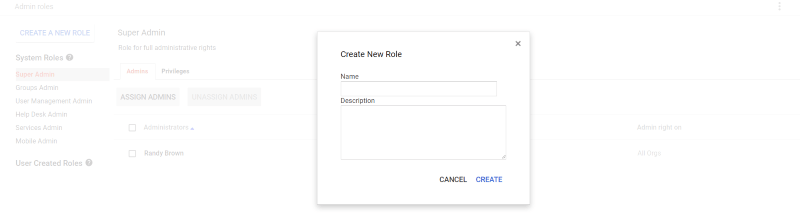

The Admin Roles lets you create new admins and assign their roles within the company. Assign their console and API privileges such as organizational units, users, security, groups, domain settings, reports, support, services, etc. The person who sets up the account is the Super Admin.
Domains
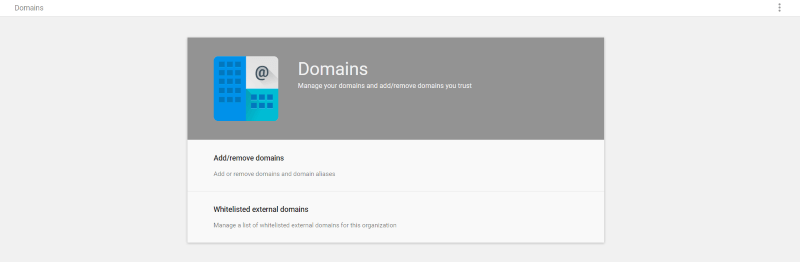

The Domains settings let you manage your domains. Add or remove them and whitelist external domains. The domain that you used to set up the account is the primary domain, but you can add aliases and create email addresses for any of the domains.
Data Migration
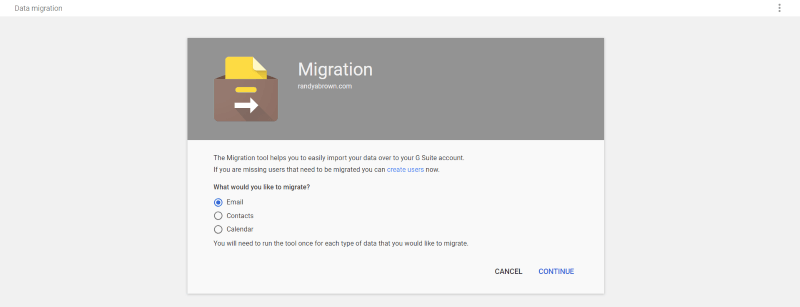

In Data Migrations you can migrate your email, contacts, and calendar. This is one of the more important areas to set up if you currently have users on a different service. It will migrate different types of mail servers and protocols. For email I recommend each member forward their emails, import old emails, import contacts, add a signature, and organize their inbox with labels and filters.
Ending Thoughts
G Suite has a lot of features for businesses of all sizes. It isn’t that difficult to set up. Most of the apps and features are enabled by default but you can customize each one individually if you want. What will take the most time is migrating your current data so that users won’t lose emails, contacts, and their calendar. Fortunately, this isn’t that difficult to do either.
Considering what G Suite provides at its price-point, and how easy it is to set up for business, it’s easy to see why it’s so popular.
We want to hear from you. Do you use G Suite for your business? Let us know what you think about it in the comments.


I believe the APP building capabilities of Google MB are still unrated. Hopefully more developers will take action and advantage of it.
Great article Randy!
Nice tips, Google has narrowed the features gap from what it was years ago, G Suite’s docs and slideshow options still remain more limited than Microsoft’s Word and PowerPoint. So if you feel the need for every possible feature just in case, Office is the better choice.
G Suite was built for the internet — no surprise there, given Google’s post-PC heritage. That approach has informed its applications, which work on the cloud. It also means that your company won’t ever lose data or documents because all the changes on Google documents get automatically saved and backed up to a Google cloud. All your team needs is a web browser on a computer or mobile device with internet access.