So you’ve decided to start an online store, but where do you begin? The first thing you will need to decide is how you’ll create and set up your store. There are dozens of eCommerce platforms available to you, so how to wade through the variety of the best eCommerce platforms to make your decision?
Some of the most popular eCommerce platforms include WordPress with WooCommerce, Magento, Shopify, and PrestaShop.
Choosing the right eCommerce platform for your online store is an important decision as you’ll likely stick with one platform for several years, if not forever.
If you’re ready to make money online by either selling products or services, setting up an online store is the way to go. The form that your online business takes will largely influence which eCommerce platform will suit your business needs. You can choose from an all-inclusive, robust and scalable eCommerce solution like WordPress, or consider a more contemporary but limited option like Shopify.
In the following post, you’ll learn the difference between WooCommerce and other leading eCommerce platforms. You’ll get a good ‘pros and cons’ comparison between the available options so that you can make an informed decision.
We’ll discuss the top eCommerce platforms for building an online store:
- WooCommerce
- Shopify
- Magento
- PrestaShop
What to look for when selecting an Ecommerce platform
Choosing an eCommerce platform can be a tricky decision. There are several things to keep in mind when making your decision:
- Technical skill level: Where are you in your level of technical expertise? Are you code-savvy, could you customize your own platform if needed, or are you an absolute beginner that should opt for a visual, code-free editor?
- Payment methods: Which payment gateways or payment processors do you need for your online store? For example, I am based in South Africa, where Stripe is unavailable. If I want to build an online store that sells and ships internationally, I need to select an eCommerce platform that supports a gateway other than Stripe, for accepting and processing international credit card payments. When considering payment gateways, also think about your target market and how they’d most likely pay.
- Complexity of your store: Is your store a simple store selling physical or digital products, or do you require more intricate selling processes or advanced functionalities?
- Budget: Do you have a lot of business capital to invest in your online store, or do you need to be a bit modest or conservative with cash before making sales?
- Scalability: Can you grow your online store as your business and brand grow?
Depending on the nature of your business and the products or services you’ll be selling online, you may need to pay special attention to other eCommerce platform variables such as shipping, taxes, invoice systems and dropshipping availability.
For our comparison, we’ve taken the following variables into account:
- Features: What features come with the eCommerce platform by default
- Price: What is the basic start-up price involved
- Ease of use: How easy is it for a newbie user to use the platform, and also, how easy is it for custom work to be done
- Payment gateways: How many payment gateways are available for the platform, and what are the charges involved
- Extensions: Are there add-ons or extensions available for the platform
- Scalability: How easy is it to scale your online store
WooCommerce
What is WooCommerce?
WooCommerce is the eCommerce extension of WordPress. Created by WooThemes and now owned by Automattic, the company responsible for WordPress, WooCommerce integrates seamlessly with the WordPress eco-system, combining a robust eCommerce solution with the already easy to use CMS.
This is the WooCommerce home page
As open-source software, WooCommece can be customized to create just about any advanced functionality. The eCommerce platform is one of the leaders in the space, so it is widely known, and there are thousands of professional WooComece developers available to help.
Features of WooCommerce online stores
Powering millions of online stores, WooCommerce ships with various features designed to help you manage your sales, inventory, shipping, and more. It integrates with an array of leading payment gateways and includes its own processor called WooCommerce Payments.
WooCommerce is compatible with most, if not all, WordPress themes. You can choose to either create a WordPress website and then integrate the WooCommerce package, or use a WooCommerce-ready theme to build your store from the start. The best thing about using the WordPress and WooCommerce combination is that you can keep expanding your site and store as your business grows.
Although WooCommerce is a free plugin that provides everything you need to manage your online store, there are many extensions available if you want to add specific features or advanced functioning. If you need it to do something that isn’t doesn’t do out of the box, you can add it with plugins or create your own code.
WordPress and WooCommerce have massive global footprints. You can find a pro WooCommerce developer with ease, should you require help. As WordPress and WooCommerce are so popular, there is plenty of documentation, tutorials, blog posts and podcasts.
Price
While the WooCommerce plugin is free, there are costs involved in owning and managing a WordPress website and WooCommerce online store. For a self-hosted site, you’ll need to pay a domain name (starting around $15 per year), hosting (starting around $8 per month), and an SSL certificate (around $70 per year). There are also managed web hosting plans available for those seeking a more premium offering. Once those are set up and running, both the WordPress and WooCommerce software are free.
There are some free themes available for WooCommerce, ranging from free to several hundred dollars. You may want to purchase a premium one as they generally look better and give you more design and development options to work with.
Next, there are WordPress plugins and WooCommerce extensions that you may want to invest in. WordPress plugins will add advanced functions to the back-end of your site or improve the look and feel of the front-end. WooCommerce extensions will offer eCommerce-specific functionality for your store.
Both themes, plugins and extensions can come at a price, so keep these setup costs in mind for your budget.
Then, if you are looking to create custom functionality not available in a plugin or extension, you can enlist the services of a WooCommerce developer. If you suspect you’ll need to add custom work to your online store, keep these costs in mind.
Payment gateways
WooCommerce offers a number of default payment gateways, including PayPal, Stripe and their very own WooCommerce Payments. It also includes easy-to-setup functionality for direct bank transfers, cheques and cash on delivery. These can easily be configured from within the plugin settings, or via the setup wizard.
WooCommerce also has support for other payment gateways. Some notable payment gateways include Amazon Pay, Authorize, PayFast, Square, FirstData, WorldPay, Sage Pay, Chase, and lots more. Each of the payment methods has its own costs per transaction, which averages 2.9% + 0.30. These can be integrated via extensions, some of which may come at a cost. The extent of payment gateways offered is impressive. They span multiple regions and even include lesser-known payment gateways.
As WordPress is self-hosted, the eCommerce platform itself does not charge a transaction fee, unlike Shopify, whose fees can be up to 2% of the transaction. With WooCommerce, you only pay the transaction fee of the payment gateway itself.
Ease of use
WooCommerce is a plugin that needs to be installed on a WordPress website. The plugin is added just like any other WordPress plugin, so it’s not too complicated.
WooCommerce has a bit of a learning curve. There are plenty of settings that need configuration. Setting up shipping and taxes can be confusing the first time around, but thankfully, there are plenty of setup guides and tutorials. WooCommerce includes a setup wizard that’ll run you through the main configuration steps. This makes getting up and running a bit easier. Once you set up one WooCommerce store, you’ll have the process waxed, and it’ll be easier the next time around.
It’s easy to customize your store once it is up and running. You can add pretty much any custom feature or special functioning thanks to the WordPress plugins and WooCommerce extensions.
Themes
There are countless free and premium themes available to WordPress and WooCommerce users. WooCommerce will work on almost all WordPress themes.
Free themes can be installed via the WordPress dashboard or via the WordPress Repository, while premium themes can be purchased via a marketplace like Envato Market or directly from a WordPress theme developer like Elegant Themes.
One of the easiest ways to create a WordPress website and a WooCommerce store is to use a drag and drop builder. These visual builders are easy to use as they let you construct a page, post or product layout exactly as you want. Unlike other eCommerce platforms, whose themes cannot be customized as easily, using a page builder to create your online store gives you so much freedom.
Find free or premium themes via the WooCommerce Theme Store
Our favorite WordPress theme is the Divi theme. It is WooCommerce-ready and includes an assortment of WooCommerce-specific modules. You can add Shop modules, Product display modules and more at any point in your WordPress website, not just on eCommerce pages. You can also use the Divi builder to design WooCommerce product pages element by element.
Even though Divi includes WooCommerce modules, it is not exclusively an eCommerce theme. This means that, when you buy Divi, you’ll be able to construct a layout for your online store, but there won’t be a set ‘template’ for you to enter your content (text, imagery and product details).
For this sort of functionality, you’ll need a WooCommerce-ready Divi child theme. If you need some info on how child themes work with WordPress websites, read this guide.
One of our most popular WooCommerce child themes is Divi eCommerce. It has a beautiful design, plenty of conversion-optimized elements and a fully set up WooCommerce store, ready and waiting for you to enter your product data. Check out the Divi eCommerce live demo.
How beautiful is the Divi eCommerce homepage? We love this child theme!
Extensions
Although WooCommerce is free, you can purchase extensions to create the online store with the exact features you want. WooCommerce extensions are specifically for eCommerce functioning, while WordPress plugins can be general and related to the website, not just the online store. Plugins and extensions can be free or premium.
Find free or premium extensions via the WooCommerce Extensions Store
Extensions can satisfy an array of eCommerce requirements, including store enhancements, adding payment gateways, improving marketing strategies, deeper reporting options, store management, and lots more.
There are thousands of plugins and extensions readily available; however, if you don’t find what you’re looking for, you can hire a wooCommerce developer to create custom functionality for your store.
Scaling
One of the best things about WordPress and WooCommerce is that both eco-systems are geared for growth. If you want to increase the number of products you sell, add a membership feature or start selling online courses as part of your product suite, you can easily build anything you like within your WordPress playground.
As your store grows, you’ll need to increase the resource capacity as your traffic increases, along with your transactions. If you’ve been using shared hosting, you may want to consider bumping up your server to a managed WordPress solution.
Scaling your WordPress website and the WooCommerce online store is easy because it is 100% your own and not tied up in a third-party service provider. There are no tiered plans that you suddenly need to adapt to, and no additional subscription costs. As you’re in full control over your site, you can decide exactly how you’d want to see it grow.
Why we recommend WooCommerce
We are avid WordPress and WooCommerce users and have been for some time now. We love the flexibility and scalability that these two technologies present.
From an ownership point of view, WordPress and WooCommerce are self-hosted so your entire online presence is yours and yours alone. Even though there are extra considerations such as hosting and
maintenance, having full ownership over an online presence is a big selling point in our opinion.
There is a learning curve to WordPress and WooCommerce, but this is overcome with relative ease. Once you’re over the hurdle of the first online store set up, you can set up countless online stores relatively cost-effectively with confidence.
Read some of our pros and cons for WooCommerce:
Pros of WooCommerce
- Together with WordPress, you have two open-source solutions that are completely free to use. If you know what you’re doing, you can create an online store relatively cost-effectively.
- First-time users may be overwhelmed, but if you explore the back-end with patience and curiosity, it’ll become second nature in time. WooCommerce includes an easy to use wizard to guide users through the initial setup steps. Due to the size of its footprint, there’s so much information available on WooCommerce, including support forums, documentation, tutorials, video walkthroughs and more. If you ever get stuck, you’re guaranteed to find a solution online. If not, there are countless WooCommerce groups and online support forums where peer developers can help out.
- WooCommerce and WordPress are industry leaders in their respective regards. The tech has a global following, complete with hundreds and thousands of developers continually adding to the open-source software. There are thousands of themes, plugins and extensions available for you to use, a large majority of which are free.
Cons of WooCommerce
- WooCommerce rests on WordPress, which is not exclusively an eCommerce platform in itself. You can create a standard website, a blog, a membership site or a course site all through WordPress. Some business owners or developers may feel like this is overkill and prefer a more focused eCommerce offering, like PrestaShop, which at its core services online stores.
- The WordPress back-end interface is quite dated. The introduction of the Gutenberg editor introduced a more modern look and feel to the post editor; however, the rest of the back-end looks quite tired. In comparison to more contemporary platforms like Shopify, WordPress and WooCommerce don’t have a sleek interface, which could be a deterrent for some users wanting a more trendy feel.
Shopify
What is Shopify?
Founded in 2004 as an online store selling snowboards, Shopify, a subscription-based all-in-one platform, has grown to become a brand leader in the eCommerce space, powering over a million businesses in countries all over the world.
Predominantly an eCommerce platform, Shopify lets you build an online store to start selling products or services. You can also choose to set up a standard display website and include a blog feature.
This is the Shopify homepage
When designing the online store, there are over 70 free and premium (paid) themes to choose from, all of which can be customized to fit any brand identity. All of your inventory is managed from one single platform, and you never have to worry about some of the more technical aspects of owning a website presence, such as hosting, backups, security and caching.
One of the main selling points of Shopify is that it requires no code to set up. If you want to start selling within a few hours, you can. In this regard, it makes for an extremely popular eCommerce platform option, particularly for newbies and first-time eCommerce entrepreneurs.
Features of Shopify online stores
Shopify works great for small to medium-sized businesses. It’s easy to set up and start selling, so it suits users without code knowledge well. Almost everything that you need comes already-integrated into the store. From hosting to theme customization, performance analytics and more, once a basic Shopify store is set up, it’s easy to expand on your offering with several third-party extensions.
Through Shopify, you can sell physical or digital products. For physical stores, there is a Point of Sale (POS) system inclusive of a card reader – one can be purchased via Shopify or you can use your own – that is perfect for brick and mortar stores.
Depending on the subscription plan you select, you can manage unlimited products and track the sales. Shopify includes various sales management features such as refunds, abandoned cart recovery, real-time sales statistics and email templates. There are also several marketing features such as discounts, coupons, gift cards and more.
Price of Shopify
Unlike WooCommerce, Shopify runs on a monthly subscription model. There are an array of pricing plans to choose from. These plans include a domain name, website, optional blog, SSL certificate, 24/7 customer support and various additional features depending on the plan of choice.
- Shopify Lite $9 per month: A great option if you only want to run Shopify eCommerce functionality through a site not set up through Shopify itself. With this account, you can include eCommerce functionality on a Facebook page or an existing website.
- Basic Shopify $29 per month: This is the cheapest plan available for an all-inclusive eCommerce solution. Here, you can have two staff accounts with access to the Shopify store.
- Shopify $79 per month: This is the standard plan and is best used for medium-sized and growing businesses. On this plan, there is an allocation for more staff accounts, and you gain access to professional reporting.
- Advanced Shopify $299 per month: Ideal for larger businesses wanting to scale. The Advanced Shopify plan includes multiple staff accounts, advanced reporting methods and third-party calculated shipping rates.
- Shopify Plus Price on request: This option is for large-scale enterprise-level businesses that require a custom solution. There is no set pricing model here; instead, merchants will need to request a custom quote.
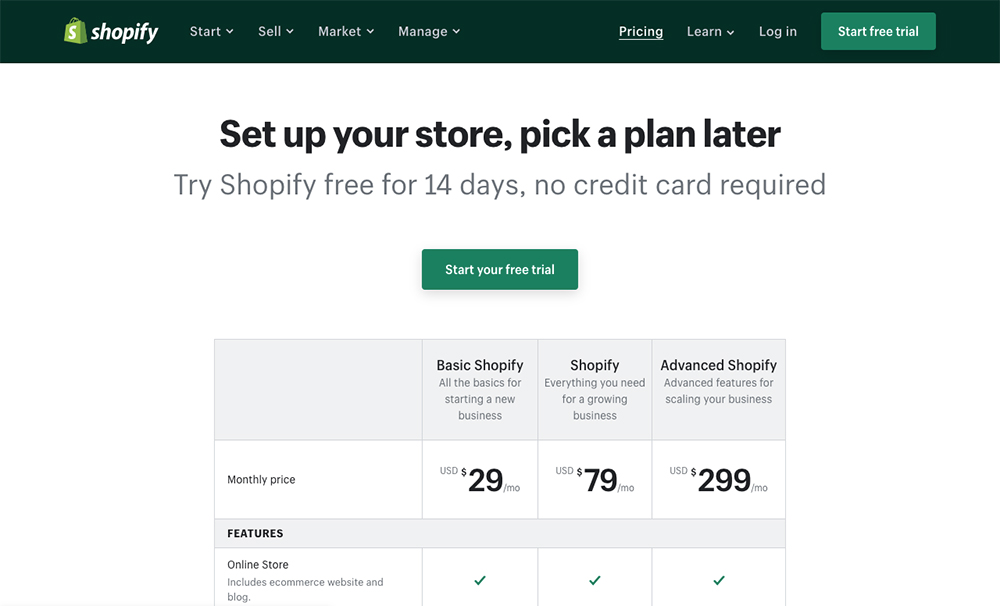
Compare the Shopify pricing plans
For a set fee, you can have your website, hosting, support and more all bundled into one neat package. One key thing to note is that, on top of the monthly subscription fee, there are also payment processing costs (more on this in the next section).
Third-party add-ons and extensions are available as separate purchases. These costs, together with the monthly subscription and payment charges, means that, as your store grows, the running cost of your store will certainly increase. If you are successful, you’ll outgrow the Basic plan and find yourself paying more. The price will increase as your store grows, which can be a drastic increase in fees over time.
If you’re curious about Shopify, there is a free 14-day trial that you can test drive the eCommerce platform out before fully committing to a payment plan. You can make a demo website, test out the site builder and contact the support channels as part of your research strategy.
Payment methods
Shopify includes its own built-in payment gateway, named Shopify Payments. From a customer’s perspective, Shopify Payments are easy to use as they process most major credit cards. Shopify Payments charge a flat rate for online and in-person credit card transactions of 2.9% + 30 cents for the Basic plan, decreasing slightly per each transaction for higher, more advanced plans.
If you need an alternate payment solution, Shopify integrates with plenty of other leading payment gateways, including PayPal, Stripe, Amazon Payments, Authorize, FirstData, 2CheckOut, and more. The catch here is that, although these payment gateways can be added and set up for free, they’ll come with a hefty transaction fee of 0.5% to 2.0% depending on your payment plan.
For example, if you’re on the Basic plan of $29 per month, and you’ve selected Stripe as your payment gateway, you’ll be paying the flat rate for credit card fees, as well as 2% of the transaction cost for the third-party payment. To offset these transaction fees, you can decrease the single transaction fee to 0.5% by purchasing the Advanced Shopify plan of $299 per month.
By keeping all transactions ‘in-house’ with Shopify Payments, you’ll save on the effort of connecting a third-party payment gateway such as PayPal, for example. However, this payment method may not fit your store or your customer’s requirements.
Ease of use
Shopify is relatively easy to set up and start using. Shopify stores can either be exclusively an online store or they take the shape of a website with a blog feature.
Once you have selected a subscription plan, domain name and theme, you can start adding your information and creating or importing your product listings. With Shopify, you don’t need to worry about technical processes such as hosting, servers, caching, backups or similar. All of these are taken care of for you in the subscription plan.
Once you have completed the core setup, all of the necessary pages, such as the shopping cart and checkout pages, are created automatically. When you are ready to create page, post and product layouts, they can be assembled using the intuitive editor.
Shopify’s drag and drop visual editor is powerful and easy to use. It lets you place content (images, text, product displays) in demarcated areas within a layout. You have a somewhat limited design ability here, as you can’t change the core interface without using an extension or editing the theme files.
On the one hand, this will be limiting for designers and developers who have a vision in mind and want full creative freedom over the layout they’re designing. On the other hand, newbie users will know exactly where to place their content, and won’t be overwhelmed with too many design options or the ‘curse of the blank page.’
Tweaking the Shopify interface is a bit more challenging. In order to do this yourself, you’ll need to learn their front-end programming language, Liquid. Alternatively, you can find a Shopify developer or third-party agency.
If you ever get stuck, there are countless resources, tutorials, community forums and a 24-hour support channel available to you.
Themes
To help eCommerce entrepreneurs get started, Shopify ships with a collection of pre-made themes. These themes are available in both free and premium versions, with premium paid themes averaging around $180.00 per purchase.
Once you’ve bought a theme, it is quick and easy to install, and then can be customized to fit your brand identity. Again, you’ll have to ‘color within the lines’ of the template and can’t stray too far away from the initial, original design.
Find free or premium themes for your Shopify website
Extensions
Once your online store is ready to make sales, you can expand on its functionality using a range of extensions.
There are hundreds of extensions in all shapes and sizes. They can satisfy various tasks such as marketing, sales, social media, shipping, inventory, accounting, customer service, reporting, or just about anything.
Extensions range in price; some are free while others with more advanced functionality come at a cost. When choosing an extension, look at the existing customer or user rating to make your decision. Also, keep in mind that while some extensions are once-off purchases, others are monthly subscriptions. These will also drive the cost of operations up.
Scaling
If you’re a successful eCommerce entrepreneur, you’re going to want to scale your online business to build an empire. You need to make sure that, when you reach the point of expansion, that your online store can grow with your business vision.
Shopify is an excellent solution for small to medium businesses, but there are some things to consider when transitioning out of the current realm of operations into a bigger space.
If you find yourself on the Shopify Basic plan, needing more resources or extra features, you can always upgrade your plan. If you need more than what’s offered on the Shopify Advanced plan, you enquire about Shopify Plus, the enterprise-level eCommerce solution for mega brands.
While this all sounds great, especially since all of the technical concerns are handled by Shopify, the process of scaling a Shopify store will drive your business costs way up. There is no pay-as-you-go option here. You’ll have to jump between the three plans, between $29, $79 and $299 a month.
Still, even with these prices, you won’t have to hire a technical team as these aspects are included within Shopify’s offering, but if you plan to scale your Shopify store, plan ahead and keep the financial implications in mind.
Shopify vs WooCommerce
Both Shopify and WooCommerce are great, powerful eCommerce platforms, but the final decision comes down to your needs. One of the main differences between Shopify and WooCommerce is the platform premise.
Shopify works on a subscription basis. You pay a monthly running cost to the eCommerce platform and don’t have to worry about the technical aspects mentioned above.
This, together with the fact that customizing themes and adding site content is easy, makes Shopify a truly great option for non-technical web users. If you’re happy to relinquish some control and ownership of your site, and you’re okay with paying a monthly fee that, as your business grows, is bound to increase, then Shopify is for you.
WooCommerce is one of the top free open-source eCommerce platforms, offering a free online store extension to an existing, up and running WordPress website. You have full ownership and control over your site, meaning that you own everything relating to your business.
The trade-off is that you have to manage and maintain the site, taking technical things into consideration such as hosting, servers and so on. Besides the running costs of owning a website, WooCommerce’s plugin is free.
If you’re considering whether to use Shopify vs WooCommerce, have a look at the final Shopify pros and cons to make your decision:
Pros of Shopify
- Shopify is quick and easy to get set up. If you know exactly what you want to create, you can, with the help of a theme, get your online store into gear in just a few hours. Shopify has a very gentle learning curve, the dashboard is quick to navigate and the drag-and-drop interface is easy to use.
- As technical aspects such as hosting, domain purchase, caching, security and performance are bundled into the monthly fee, this means that you have very little to worry about, other than the process of running your store. Caching and security are two of the most intricate processes for a website and online stores, so not worrying about these hassles is a relief.
- If you already have an existing website on another platform and want to incorporate the Shopify purchase experience, you can opt for the Lite version for only $9 per month. Here you can embed a Shopify purchase button to your site and turn a display website into an online store with very little hassle.
Cons of Shopify
- The SEO reporting tools for Shopify are not as robust as other platforms. While there are some SEO extensions, these don’t seem to satisfy the same SEO requirements as made available through WordPress plugins. Without stellar SEO tools, the content on your Shopify website will have to work an extra bit harder to bring you the same organic traffic returns. Alternately, you need to consider a more edgy marketing strategy or strategies and not rely solely on content-led marketing.
- As Shopify is a sales platform, first and foremost, it falls short on the blogging front. You can publish posts, display categories, allow comments and include a few levels of SEO metadata, however, you won’t be able to get blog-related analytics, archives or other advanced content publishing and sharing features. Blogging is the gateway for organic traffic strategies, so if displaying well in search results is one of your goals, consider an alternate eCommerce platform, one that is optimized for content marketing.
- For those business owners who want to know that they own, run and manage everything, Shopify may not be the best solution. Where typical hosting and server packages are owned by the business owner, in the Shopify model, these are bundled into the subscription cost. If you’d like to own your online property in entirety, it would be better to consider a different eCommerce platform.
Magento
What is Magento?
Like WooCommerce, Magento is an open-source eCommerce platform. Created by Adobe, the team behind Photoshop and other popular creative apps, Magento has everything you need to create and manage an online store.
This is the Magento homepage
Magento is available in both a free self-hosted version and a paid cloud-hosted version which includes additional premium features and priority support.
Features of Magento online stores
Magento is a high-quality eCommerce platform that is built for performance at any level. It can satisfy a small online shop managing a modest range of products, or it can accommodate enterprise eCommerce brands with a vast inventory.
With everything you need to create and manage an online store, Magento handles payments, provides shipping options, offers analytics and business intelligence features, security benefits and much more.
Once your store is ready to go, you can design the front-end by using one of the templates on offer. Online stores built with Magento can easily be expanded through upgrades and extensions. The software is open-source, which means that you can take the API and customize it to suit your needs.
Price of Magento
Magento ships in two versions. Depending on your budget, you can select which is best for you.
- First, there is the Community edition. You can download the software package and install it on a server from any host of your choice. This version of Magento does not include support or the full commerce suite of features, so you’ll be expected to front the costs for hosting, domain name purchase, themes, development and so on.
- Then, there is the paid plan of Magento Commerce. There are several solutions available to choose the features you need from small business to enterprise level. There is no clear-cut pricing for the software displayed on the Magento website, however, others have reported that the enterprise level is above the $20,000 per year range. This piece tag comes with benefits including top-notch support, high-performance cloud hosting and additional features that otherwise would have come in the form of a paid extension.
Although you can use your own host for the scaled-down, free Community version, it may be better to consider a more robust hosting option. A standard, shared server may not cut it, and you may need to consider VPS hosting or a cloud-based option. Using Magento’s paid hosting might be a better choice because of the difficulty of maintenance. Also, if you need to scale your store, you’ll probably eventually need to move to Magento’s premium hosting anyway.
Finally, when considering budgets, keep in mind the cost of purchasing premium themes and extensions, as well as whether you’d need to hire a Magento developer for any front or back end site changes.
Payment methods
Magento offers a broad range of payment gateways, including PayPal to Authorize.net. There are also a few extensions available for integrating with other popular payment processors such as Stripe, WePay, Google Checkout and more.
If there isn’t an extension for your preferred payment gateway, you can always enlist the services of a developer to build a custom extension for you.
Ease of use
Magento is a complex platform. It has a steep learning curve and has a slew of advanced configurations for the setup. As a result, it may not be the best option for beginners.
If you’re looking to save on costs and are opting for the Community edition, you’ll need to know your way around a server to install the software field. This step is made more complicated as most hosting companies do not include an easy to use pre-installer, as is the case with WordPress.
Also, the Community version does not include support, so you’ll be on your own if things go wrong, or you’ll need to hire someone to help you.
If the learning curve or complexity of the platform are not deterrents, or you are or are hiring an experienced developer, Magento may suit your needs.
It’s a very powerful eCommerce platform that offers many built-in features that negate the need for extensions. Once your software is installed on the server, processes like adding themes or extensions can be a bit tricky, so if this is your first time, look for tutorials, video walkthroughs, or Magento documentation online.
Themes
There are a number of Magento themes available in the Magento Marketplace. These themes range anywhere from below $70 to above $400.
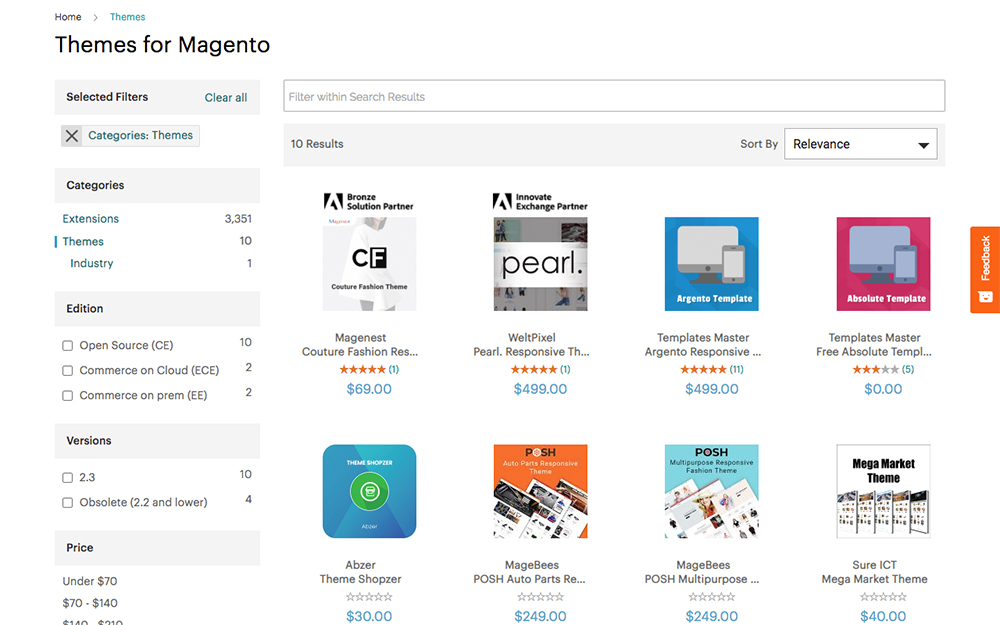
Find free or premium themes via the Magento Marketplace
Extensions
When you reach the point that you need custom functionality on your site, you can consider using extensions. With these extensions, you can add new features and tools into your eCommerce store.
There are loads of free and premium extensions available for Magento. Each of the extensions have been developed for the specific Magento platforms and editions of Community or Enterprise. If you are a keen developer, you can create your own extensions and sell them in the Magento Marketplace.
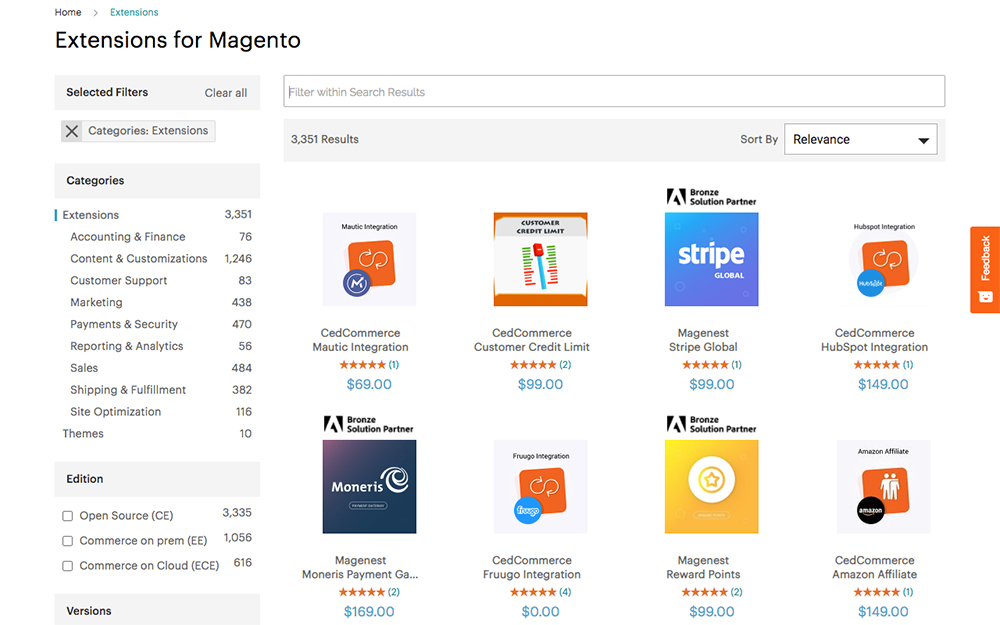
Find free or premium extensions via the Magento Marketplace
Scaling
The scalability of an eCommerce platform is a significant consideration. If you want to expand your brand and offering, you’ll need to select a scalable eCommerce platform from day one.
Magento certainly can scale to a large online store and enterprise-level, however, the costs involved can be a deterrent.
There are various plans available in the Magento Commerce suite, the enterprise-level being one of them. If your business can afford the high cost involved in this service, it may be a good idea to consider one of Magento’s paid plans.
If you are using the free Community version of Magento, you’ll need to do everything yourself, so not only will your costs rise, but the technical difficulties will too.
You’ll need to pay even more attention to your caching, performance, backups and security, and, since the Community package doesn’t include support, you’ll be doing this all on your own. If you lack the skills and technical expertise, you may need to enlist the services of a Magento developer.
As your online store grows, its traffic will increase along with the resources required by your server. If you were using a VPS before, you’ll more than likely need to move to a more robust server configuration, such as a dedicated server or cloud hosting option, to accommodate your website’s growth. The costs for these top-tier servers are high.
Magento vs WooCommerce
Both Magento and WooCommerce are great eCommerce platforms. If deciding between Magento vs WooCommerce, consider your budget, skill level and future plans for your online store when making your decision.
Magento is an incredibly powerful eCommerce platform, but it is better suited for enterprise-level business, either with an in-house development team or professional Magento developer on contract.
If you’re a serious eCommerce entrepreneur, one who has a big vision in mind and a big budget too, Magento is a perfect choice for you. On the other hand, if you have technical experience with the Magento eCommerce platform, or are wanting to learn the software, then it could also pose as a great option.
You can start your online store with Magento at a small-scale and then expand, but a small-scale, hobbyist online store will probably find more success with an alternate platform. There is an extremely complicated learning curve for Magento, so it’s not the best solution for a first-time online store creator, and not the best option for non-technical users.
Overall, Magento is extremely powerful and comes packed with many features, but it is not the easiest to use eCommerce platform.
Where Magento caters to the needs of larger online stores, WooCommerce is more adaptable and can cater to a broad range of business sizes and types, even the small entities, particularly those starting with a lower budget.
WooCommerce has a small learning curve, but once you’ve mastered this, it’s easy to set up and use. There is a bit of technical skill required, but if you want to bypass the setup and configuration step, you can easily contract a WooCommerce developer to do the store set up for you.
As WordPress and WooCommerce have large global footprints, you’ll find a developer to help you with no problem, and generally, their costs aren’t unreasonably high. With WooCommerce, you can start small, expand with extensions and scale your online store as your business grows. Scaling WooCommerce does not require moving to a higher plan or anything of the sort. Also, since the WooCommerce plugin is 100% free, you can build multiple online stores relatively inexpensively.
If you’re considering whether to use Magento vs WooCommerce, have a look at the final Magento pros and cons to make your decision:
Pros of Magento
- Magento presents a high-end eCommerce platform that caters to large business and eCommerce empires. If you want to build an extremely large online store, the Magento suite is a great option to consider. If you have the capital or budget to invest, you can opt for one of the paid plans, which will include support and advanced features, or you can enlist the services of a Magento developer to assist you.
- If you want to build a powerful online store by yourself, the open-source Community package is free to download and use. This is a great option provided you either have the technical expertise to set up and run a Magento online store or intend to learn Magento development.
Cons of Magento
- Magento is costly. Whether you’re opting for a paid plan which has high-cost implications, or you’re using the free Community version, which is labor-intensive, you won’t find a quick and easy fix in Magento.
- If you opt for the Community version route, setting up and maintaining your online store will require technical expertise. You’ll have to configure your server by yourself and install the Magento package manually. You’ll also need to invest in a powerful server, as a standard shared hosting package won’t cut it. Magento is not a user-friendly option for first-time online store creators, so unless you have Magento development skills yourself, or are willing to pay a Magento developer, you’ll probably struggle with this eCommerce platform more than other alternatives.
PrestaShop
What is PrestaShop?
Next on the list is PrestaShop. PrestaShop is another one of the open-source eCommerce platforms. It is highly customizable and gives you complete control over your online store. Like WordPress, it was developed using PHP and lets online store owners create and sell products, make sales, and track orders.

This is the PresaShop homepage
Launched back in 2007, PrestaShop is a firm choice for eCommerce developers looking to build online stores. PrestaShop can be used to build any form of website; however, its main focus is eCommerce.
Features of PrestaShop online stores
PrestaShop ships with plenty of native features, such as letting online store owners create physical or digital products, control inventory, manage orders and track sales, set up taxes, configure shipping, offer coupons and discounts, and much more. The CMS itself is easy to use.
As PrestaShop is specially geared to be an eCommerce platform, not a general website creator, the native features are explicitly designed to help users sell online. Other eCommerce platforms that are a bit more general in their offering do not include such an array of focused features out-of-the-box. Other eCommerce platforms will also charge for the same native functionality included in PrestaShop in the form of premium add-ons or extensions.
Once set up, the functionality of the store can be expanded through the use of add-ons. There are thousands of add-ons in the PrestaShop Marketplace spanning various categories, from marketing, sales, reporting and much more.
Price of PrestaShop
As open-source software, the PrestaShop package is free to download and use. Like WooCommerce, which ships as a free plugin, the subsidiary running costs of having a website, such as hosting and domain purchase, will drive up the price.
What’s important to note about PrestaShop is that the templates and add-ons come at a relatively high price. Also, there are very few add-ons or extensions that are free. In comparison to WordPress and WooCommerce, where there are plenty of top-notch free themes, plugins and eCommerce extensions readily available, the costs for setting up advanced functionalities for a PrestaShop store can be relatively high.
If you’d like to give PrestaShop a look through before committing, you can check out the live demo of a PrestaShop online store here.
Payment methods
PrestaShop comes with two default methods already installed: bank transfer and payment by cheque. These two payment methods are not the most user-friendly, so a bit of engineering is required to set up an appropriate payment processor.
PrestaShop has support for many payment gateways, including Amazon Pay, Stripe, CloudSwipe and Skrill, to name a few. These can be installed quickly from the back-end dashboard of the site. There is also support for other payment gateways that can be initiated by installing a separate module. Depending on you and your customer’s preferred payment gateways, you may need to purchase a premium module to accept online payments.
Ease of use
Once installed on a server and ready to go, PrestaShop needs to be configured from the CMS dashboard. Unlike WooCommerce, there’s no handy setup wizard, so you’ll have to figure out the configuration steps yourself. This isn’t a challenge as there is plenty of documentation online.
To make your store, you can either build it from scratch or use one of the free templates. Using a template makes designing a store considerably faster. Regardless of the templates, the PrestaShop software is not as user-friendly as some other platforms mentioned in this article.
PrestaShop has a great, global community of developers, so support is readily available to you should you require it. The eCommerce platform is also well documented with plenty of tutorials and forums for guidance.
Templates (Themes)
PrestaShop users can browse a selection of themes (referred to as templates) in the PrestaShop Marketplace as well as templates sold via third-party vendors. There are thousands of templates, each geared towards helping you build your online store. The only catch is that very few of these templates are free.
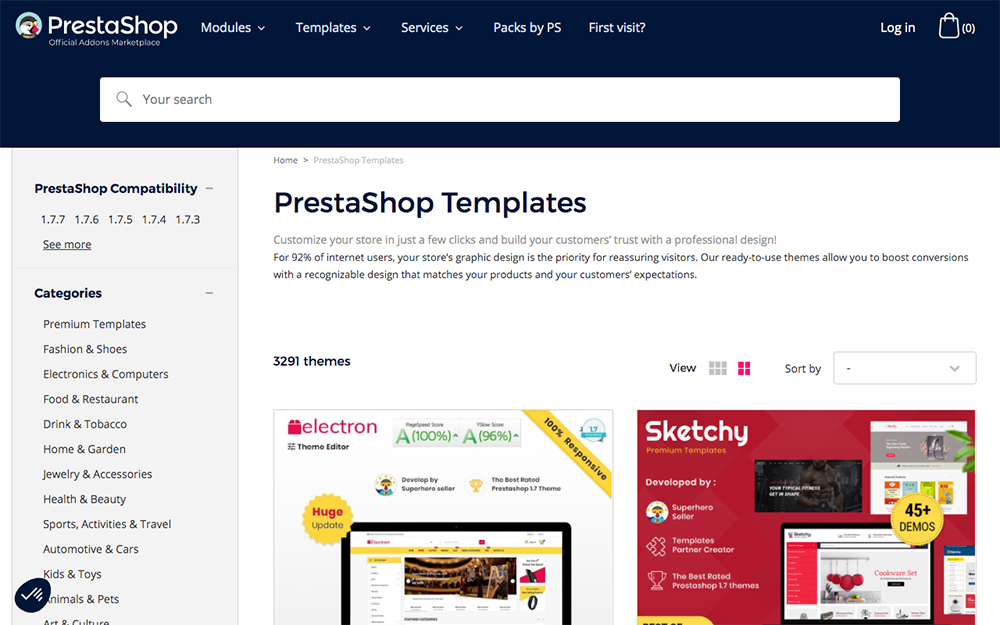
Find free or premium templates via the Prestashop Marketplace
Typically, PrestaShop templates can range anywhere from $80 to $300, so keep these costs in mind when considering the eCommerce platform for your site. The premium templates tend to look more attractive than the free ones, so you’ll more than likely invest in one.
Add-ons (Extensions)
To extend your PrestaShop store’s functionality, there are a selection of add-ons that can be purchased for a pretty penny via the PrestaShop Add-ons Marketplace.
There are thousands of add-ons available, typically as a once-off purchase, not subscriptions. The cost of add-ons can range anywhere from as low as $20 up to hundreds of dollars. For example, setting up an Amazon or eBay inventory management integration can cost over $200 each. If you’re thinking of purchasing a bunch of add-ons, make sure you budget for these expenses beforehand because the costs will add up.
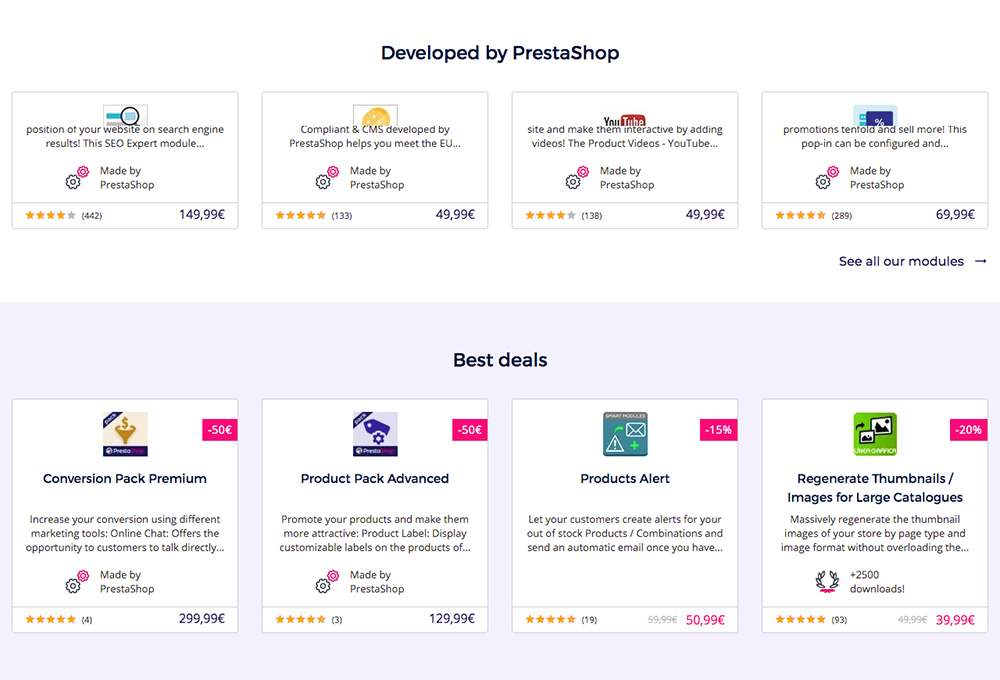
Find free or premium add-ons via the Magento Marketplace
Scaling
PrestaShop is a great option to consider if you’re thinking of building a large store. As its sole focus is eCommerce, everything about this platform is geared toward building and growing an online store.
If you find your business and online store starts to evolve, PrestaShop can easily catalog over 100 000 products and manage countless orders.
PrestaShop vs WooCommerce
If you’re deciding between PrestaShop vs WooCommerce, you may have a bit of a challenge at hand as both of these eCommerce platforms offer great value to their users. Since both technologies are open source eCommerce platforms, you can save costs in some regards and allocate budget into other spaces, should you desire.
PrestaShop is laser-focused on eCommerce. Its creators have evolved the platform with the ever-growing needs of eCommerce stores and online entrepreneurs in mind. If you know for a fact that your sole focus is to build an online store, and you want to maximize this, perhaps consider PrestaShop.
It is a robust solution that can accommodate countless products with ease. Also, you’ll get plenty of eCommerce-specific features out of the box, where other platforms would require this functionality via a paid add-on or extensions.
WooCommerce, on the other hand, presents a more well-rounded offer. As it rests on top of WordPress, you can create a super functional online presence as well as an eCommerce store. Together, WooCommerce and WordPress are an all-in-one solution that allows you to extend your business offering in various areas.
If you’re still considering PrestaShop vs WooCommerce, have a look at the pros and cons of PrestaShop:
Pros of PrestaShop
- The PrestaShop software is open-source, so it is free to download and use. You can also customize the code for your needs. There is a thriving community of supportive developers ready to offer assistance should you require it.
- PrestaShop includes some advanced eCommerce features out of the box. These are designed specifically for creating and managing an online store. Other platforms may only offer this sort of functionality via extensions or add-ons.
Cons of PrestaShop
- The PrestaShop add-ons are quite costly. What is interesting about these add-ons is that they cover both advanced eCommerce functionality and general website functions. For example, there is an add-on available for integrating the Facebook pixel with your online store. This add-on sells for €50 a pop. In WordPress, the same functionality comes in the form of a free plugin. If you’re using the Divi theme, integrating something like a Facebook pixel is already catered for within the theme package – no additional plugin is needed. The same applies to SEO software; in WordPress sites, Yoast SEO or All in One SEO Pack offer great free plugins, whereas, with PrestaShop, an add-on must be purchased.
- As PrestaShop is first and foremost an eCommerce platform, its singular focus is to publish and sell products. If you’re looking to create more of a ‘bigger picture’ online presence for your brand, you may find that the native eCommerce features in PrestaShop are unnecessary. Also, since so many add-ons are required for even basic website functions, you may have better success elsewhere.
Ending thoughts
Selecting the best eCommerce platform for your online store is a big decision. To make this a bit easier, perhaps start with the end in mind.
First, think about how large you would want your online store to grow. If you envision a mammoth online store, one that regularly turns thousands of items, consider one of the enterprise-level solutions. Next, think about how you would want your brand and business to grow. If you are offering an online store today but would like to sell courses or memberships tomorrow, consider a platform that accounts for the growth of your website as well as the online store. Finally, if you’re simply super excited to start selling products as soon as possible, consider your technical skill level and whether you’d want a code-free building experience or if you’re code-savvy and don’t mind getting a bit technical.
We hope that this eCommerce platform comparison post has helped you think a bit more strategically about how you’ll build your site. If you have any questions or comments, or, if you have an experience that you’d like to share regarding these or other eCommerce platforms, please post them below!
Thanks for reading!


Recent Comments